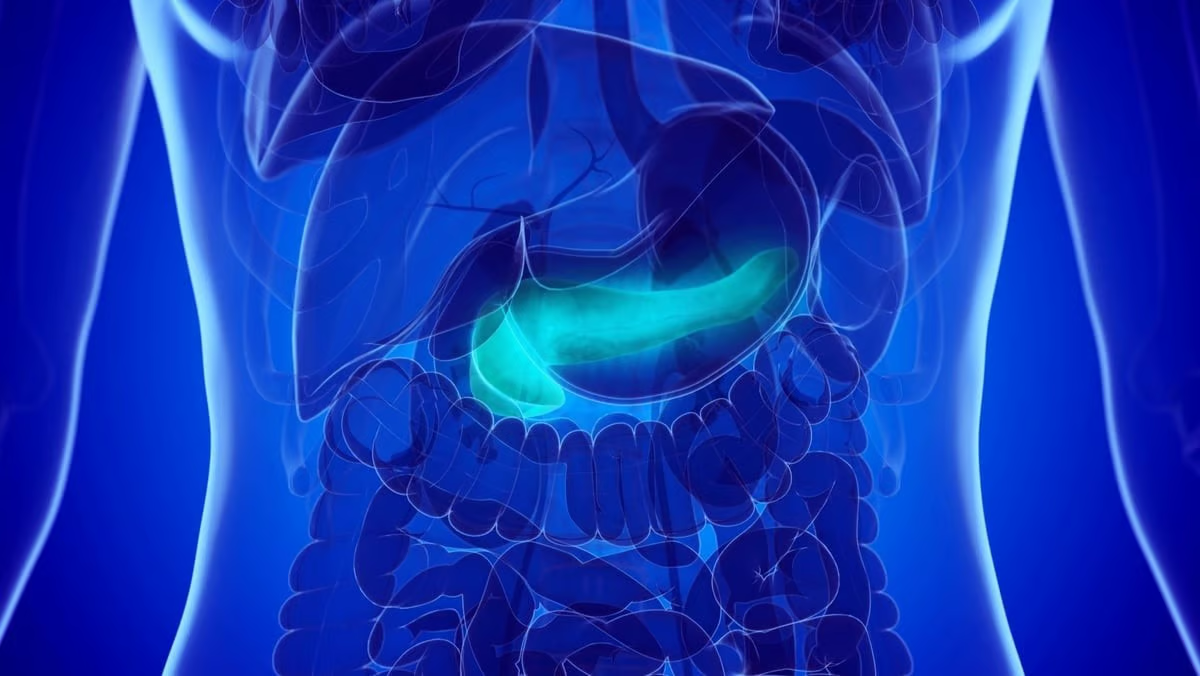
(HealthDay News) — (Tasrir) — Up to now, doctors have been cautious about prescribing semaglutide to patients with a history of pancreatitis, because they feared the drug could worsen the condition, said lead researcher Dr. Mahmoud Nassar, a fellow in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Buffalo in New York.
In fact, the drug’s prescribing information even warns about this potential side effect, Nassar noted.
“Our research highlights the safety and the potential for GLP-1 receptor agonists [like semaglutide] to reduce the risk of acute pancreatitis recurrence in individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes, challenging previous concerns and offering new hope for effective disease management,” Nassar said.
For the study, researchers analyzed data on more than 638,000 patients with a history of pancreatitis. The patients were located across 15 countries, but they were mainly from the United States.
Researchers tracked how many patients developed pancreatitis again within 15 years of starting either semaglutide or other drugs for diabetes and obesity.
The other drugs included SGLT2 inhibitors, which decrease blood sugar levels by preventing glucose from being absorbed in the kidneys, and DPP4 inhibitors, which help the pancreas release insulin.
About 15% of patients taking semaglutide had wound up suffering a recurrence of pancreatitis, compared with 24% in the SGLT2 inhibitor group, 23% in the DPP4 group and nearly 52% of patients not taking any drugs at all.
The study was presented Saturday at the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston. Findings presented at medical meetings are considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“This study provides critical insights that could change the treatment landscape for patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes, particularly those with a history of acute pancreatitis,” Nassar said in a meeting news release.
“The possibility of using GLP-1 receptor agonists more broadly offers hope for better managing these conditions, improving patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life,” Nasser said. “It emphasizes the importance of personalized medicine, where treatment decisions are tailored to the individual’s specific health profile and needs.”