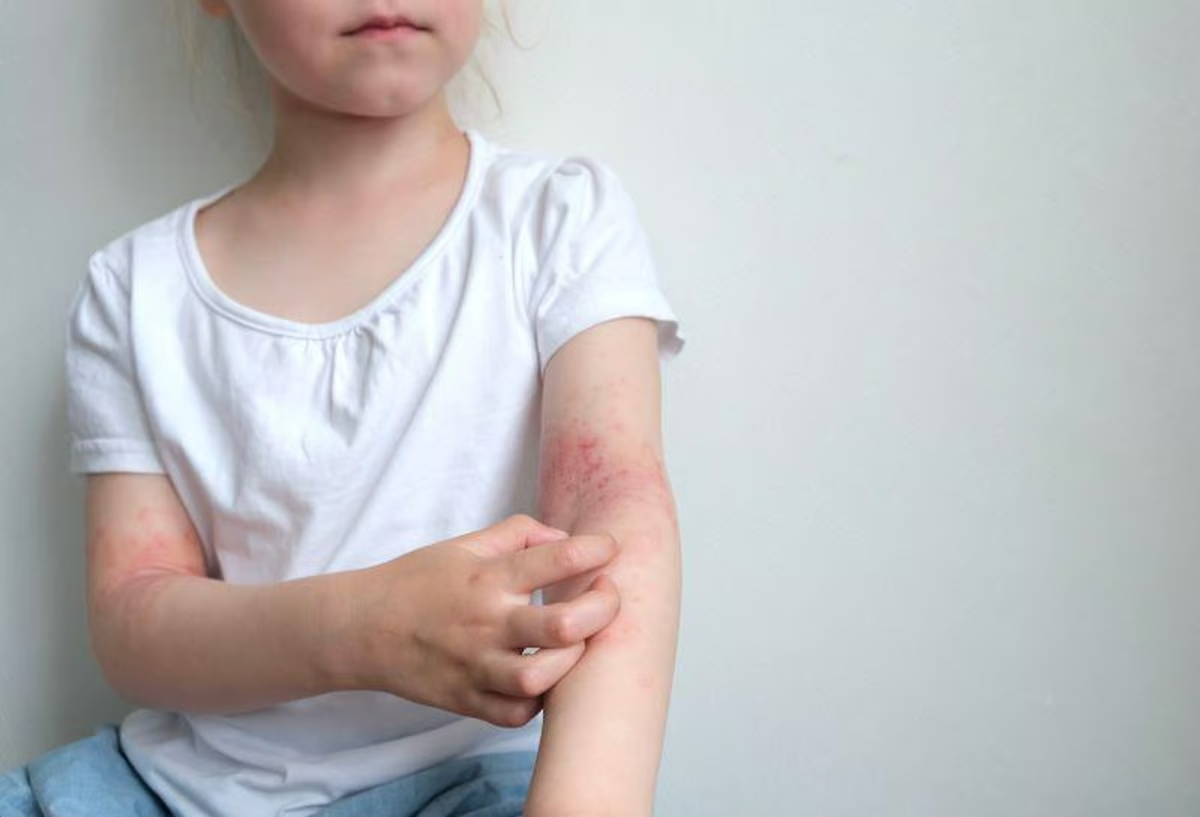
THURSDAY, May 23, 2024 (HealthDay News) — (Tasrir) — In a study involving data from over 35,000 U.S. households, children with a parent who used e-cigarettes had a 24% higher odds for eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) than kids with two non-vaping parents did.
“Our results suggest that parental e-cigarette use was associated with pediatric atopic dermatitis,” concluded a team led by Dr. Golara Honari, a clinical associate professor of dermatology at Stanford University, in California.
Her team published its findings May 22 in the journal JAMA Dermatology.
According to the researchers, there is science backing up the notion that exposure to the toxins emitted in e-cigarette vapor could trigger changes in children’s skin.
Prior lab studies have “demonstrated increased oxidative stress in human keratinocytes and 3-dimensional skin models exposed to e-cigarette fluids and aerosol residues,” they noted. Keratinocytes are cells that make up about 90% of the skin’s outer epidermal layer.
In a study involving data from over 35,000 U.S. households, children with a parent who used e-cigarettes had a 24% higher odds for eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) than kids with two non-vaping parents did.
“Our results suggest that parental e-cigarette use was associated with pediatric atopic dermatitis,” concluded a team led by Dr. Golara Honari, a clinical associate professor of dermatology at Stanford University, in California.
Her team published its findings May 22 in the journal JAMA Dermatology.
According to the researchers, there is science backing up the notion that exposure to the toxins emitted in e-cigarette vapor could trigger changes in children’s skin.
Prior lab studies have “demonstrated increased oxidative stress in human keratinocytes and 3-dimensional skin models exposed to e-cigarette fluids and aerosol residues,” they noted. Keratinocytes are cells that make up about 90% of the skin’s outer epidermal layer.